Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
Every year, many children suffer from burns and scalds in the home, and at play, many of these injuries are unforeseen, for example, a child pulls a hot cup of coffee over themselves, touching a hot pan. We will look at some further causes and the complications that may develop with these burns.

Every year, many children suffer from burns and scalds in the home, and at play, many of these injuries are unforeseen, for example, a child pulls a hot cup of coffee over themselves, touching a hot pan. We will look at some further causes and the complications that may develop with these burns.
Sunburn- Superficial
The superficial burn is where the top layers of skin (epidermis) have been burned.
This burn is caused by:
The child will be in pain, the skin is red and tender with swelling and light blistering.
5% burn or if the burn affects the airways, the child must go to the hospital.
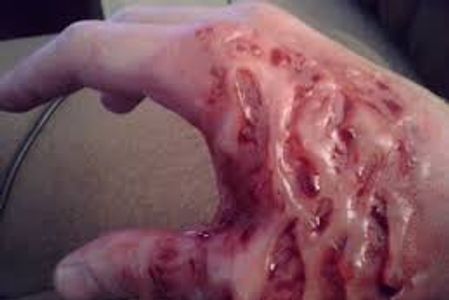
The partial-thickness burn is where the top and some lower layers of skin (epidermis & dermis) have been burnt. This type of burn is very painful and is at risk of infection; shock may also occur.
This burn is caused by:
The child will be in severe pain, the skin is raw and tender, swelling with blistering, and clear fluids will be emitted from the burnt areas. 9% partial thickness burn will cause a child to go into shock. 1% burn the child will require medical attention.
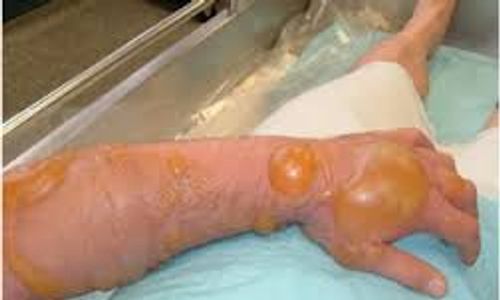
The old saying "burnt to the bone" refers a severe, deep burns, nerves are destroyed, and there is a very high risk of infection.
This burn is caused by:
The child will be in pain; however, due to nerve damage, the pain may be decreased, but that is not to say this injury is not painful. Shock may also be present.
No matter what size this burn is, the child must go to the hospital for treatment.
Now that we understand classifications of burns, how do we determine the size of the burn?
The answer is the size of the child's hand
1 whole hand, fingers included=1% of the child's body.

The rule for burns is to cool them down; however, there are certain types and locations of burns that may need to be considered, for example, chemical burns.
Important!
Ensure you protect yourself with "gloves" on this chemical could burn you.
There are many types of domestic and commercial chemicals. You must understand the principle of COSHH (Control of Substances Hazardous to Health).
Information should be labelled on the container; this information should briefly instruct the first aider on the treatment required in the event of an accident.
The rule with chemicals on the skin is normal.
20 minutes of flushing with cold water

Having anything in your eye can be stressful; however, a chemical that enters a child's eye can be very stressful and painful. No matter what, the aim is to prevent further damage to the eye and sight of the child.
The following actions should be carried out immediately.
10 minutes of flushing with cold water
Ensure you flush the eye for 10 minutes; the eye can become sore and damaged by overuse of very cold water. Wait and see how the child reacts if they show distress or mention burning, continue to wash out the eye.
Identifying the chemical is important; for example, oven cleaner will cause severe damage to a child's eye compared to washing up liquid, which can be painful at the time; however, the damage is minimal.

1. Wash the chemical away
2. Use a towel to wipe up water as it runs down the face, especially if it is a corrosive chemical.
3. Keep using water until the burning stops
4. Cover both eyes to limit movement
5. Call 999/112 if the child goes into shock or the burn is severe.

Remove the
source of heat, turn off the electric appliance if this
has caused the burn.

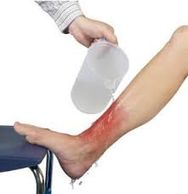
Get the child to cold water
or
Bring water to the child
Flush the burnt area for a minimum of 20 minutes.
Be careful not to use high-pressure water, as this will tear skin.
Only remove clothing and jewellery if it is not burnt to the child's skin. If in doubt, leave it and continue to use cold water.

Cover the wound with a first aid dressing, or lightly layer clingfilm over the burn.
Clingfilm should be layered and not wrapped around the burn. This prevents overheating and easy removal.

Once a burn has been cooled under cool running water for 20 minutes and then properly dressed, you generally should not apply an ice pack or cold towel on top of the dressing.
Keep dressing dry
Lay a cool pack over the dressing and elevate when possible. This will reduce heat and swelling.

Once you have treated the burn and assessed the depth and size, you must either take the child to the hospital or call 999/112. Ensure you assess the child for shock.
Take your time as you go through this assessment read the question as some have more than 1 answer. This assessment requires you to score 7 out of 10. Your score will appear at the end of the assessment, you can check your answers, and an email will be sent to you and Life Lines of the result
GOOD LUCK